A Variety of Satellites
What is a Man-made Satellite?
Before thinking about what a man-made satellite is, let’s think about what a satellite is. A satellite is a celestial body that orbits a planet. For example, the moon is a satellite for the Earth. A “man-made satellite” is literally made by a human. Sometimes we call it simply “satellite” instead of the formal term.
Hayabusa, which successfully returned asteroid samples, is not classified as a “satellite” but a “probe”. This is because the main purpose of the mission is to reach the target celestial body and “explore” it, not “regularly orbiting around the planet” to continue observations, which is the original meaning of a satellite. Basically, “satellites” often refer to those orbiting the Earth, while those orbiting other celestial bodies are often described as “probes”.
What do satellites do?
Satellites can be broadly classified according to their purpose as follows:
| Purpose | Typical Orbit | Example | |
| Earth Observation Satellite |
Long-term observation of the changing global environment (atmosphere, ocean, land and cryosphere) | LEO/GEO | • Advanced Land Observing Satellite-2 “DAICHI-2”(ALOS-2) • Global Change Observation Mission-Climate ”SHIKISAI”(GCOM-C) • Global Change Observation Mission-Water ”SHIZUKU”(GCOM-W) • Himawari-8※ • others |
| Communications Satellite Broadcasting Satellite |
Relay and broadcast of wireless communications | LEO/MEO/GEO | • Laser Utilizing Communication System (LUCAS) • Engineering Test Satellite-9 • others |
| Positioning Satellite |
Transmission of signals needed for position measurement | MEO | • Quasi-Zenith Satellite System “MICHIBIKI” • others |
※Himawari-8 is a type of Earth observation satellite, but in some cases it is classified as a “meteorological satellite,” designed for meteorological observation.
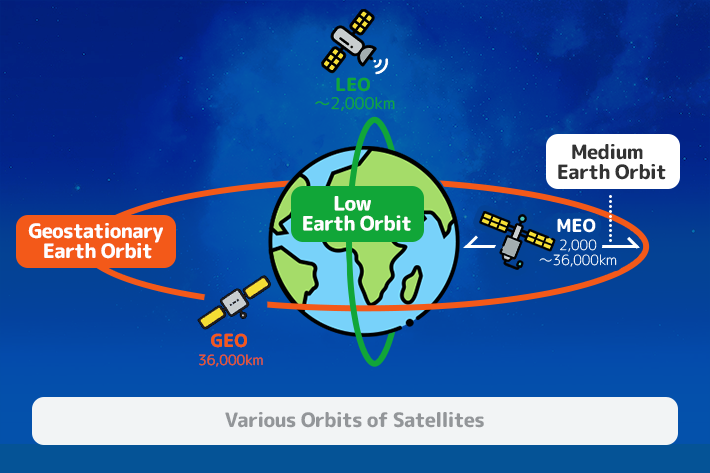
The orbits of each satellite are divided into the following three types, depending mainly on its altitude.
• Low Earth Orbit (LEO):
An orbit at an altitude of up to 2,000 km. One orbit around the Earth takes about 90 to 120 minutes. Only a small part of the Earth’s surface can be seen, but it is possible to observe at high spatial resolution.
• Middle Earth Orbit (MEO):
An orbit between 2,000 km and 36,000 km above the Earth’s surface, with a wider view of the Earth than the LEO satellites.
• Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO):
An orbit at an altitude of 36,000 km. Satellites in this orbit move at the same speed as the Earth’s rotation, so they can continue to observe almost the same location on the Earth.
Most of the satellites operated by JAXA are Earth observation satellites and are launched in LEO. Super Low Altitude Test Satellite “TSUBAME” (SLATS) was registered by the Guinness World Records for the lowest altitude by an Earth observation satellite in orbit (167.4 km).









